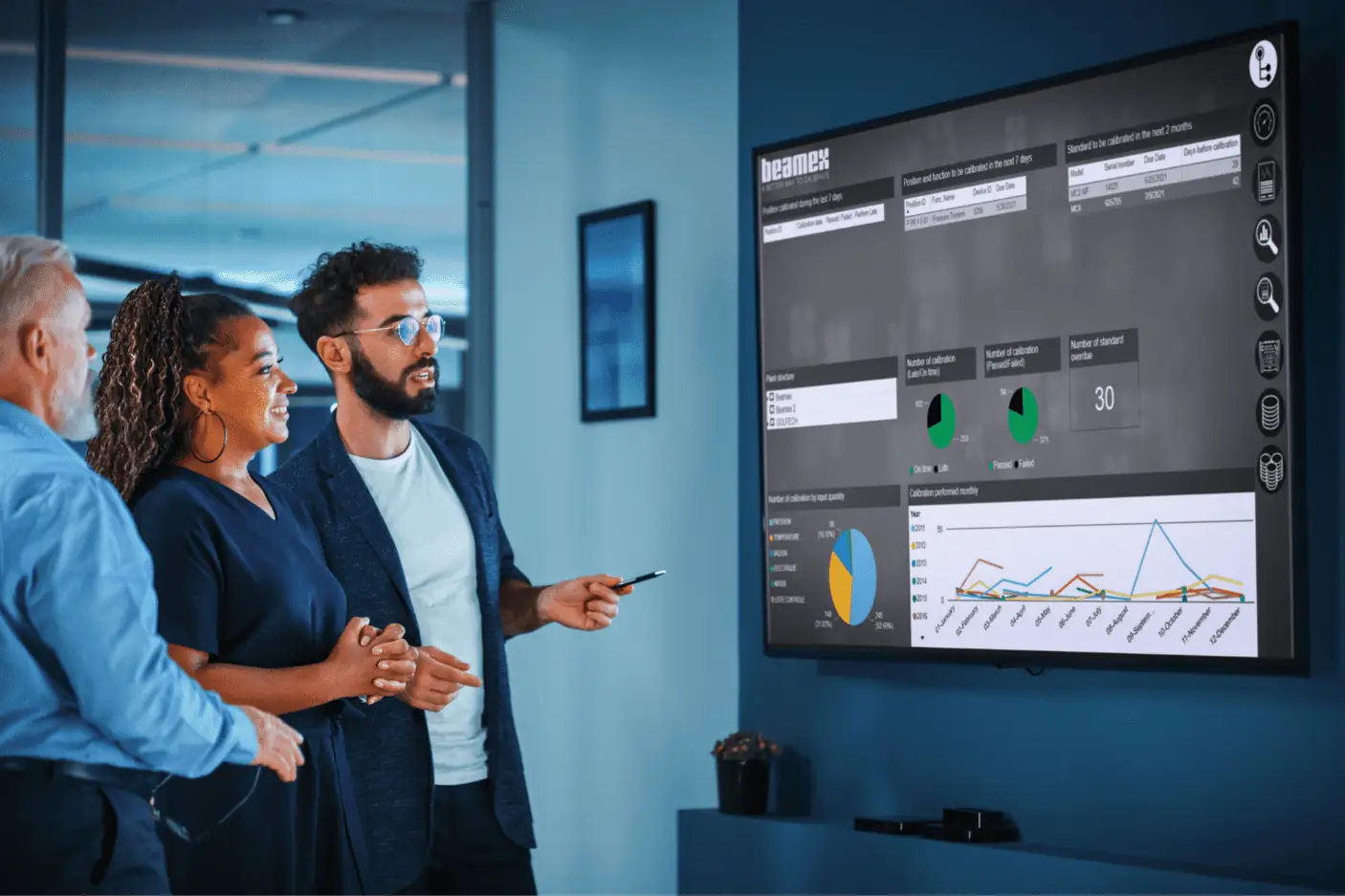
What is calibration management software?
As the manufacturing industry expands, so does the need to have greater control over management processes. As this need has increased, so has the requirement for better management of the equipment that is used to measure and control manufacturing processes. Industrial devices like weighing instruments and pressure sensors require regular calibration to ensure they are performing and measuring to specified tolerances. Given the volume of assets and equipment that need to be managed and calibrated, this can become a fairly daunting task for any equipment manager.
An automated calibration management software can make this task a lot easier. It enables the automated management and storage of all instrument and calibration data. This includes the planning and scheduling of calibration work; analysis and optimization of calibration frequency; production of reports, certificates and labels that aids in error and cost reduction, and improved organization and productivity.
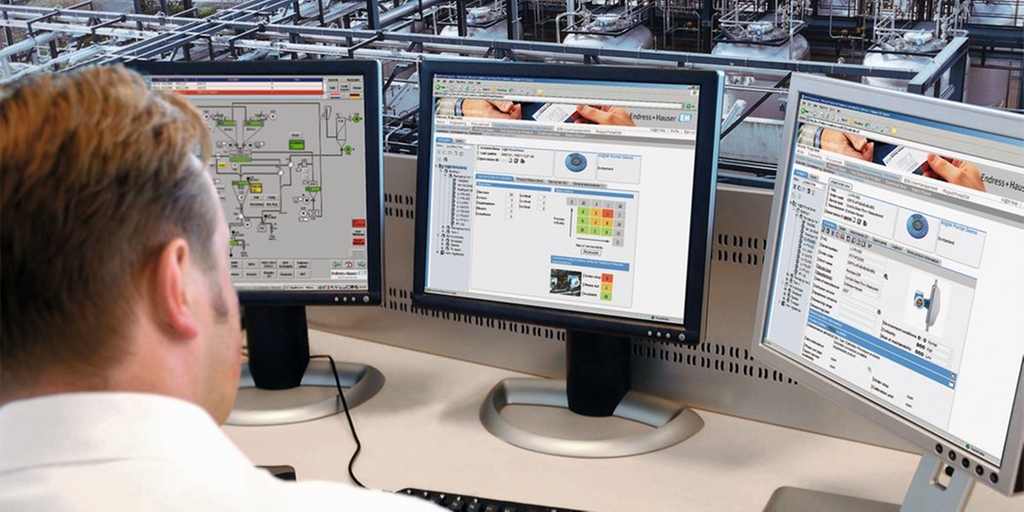

What constitutes a calibration management process?
Before we go further into the need of having a calibration management solution, its features, and benefits – it is important to consider the typical calibration management tasks that businesses have to undertake. Listed below are some steps that constitute a typical calibration management process:
1) Identification, classification, and planning
Firstly, the instruments and measurement devices that a business owns are listed. They are then classified as either ‘critical’ or ‘non-critical’ devices or their calibration range and required tolerances are identified. Decisions are then made regarding the calibration interval for each instrument. Finally, an equipment manager must identify current calibration statuses for all instruments across the organization.
2) Organization
The calibration staff needs to be organized. They must be trained in using the chosen tools and carrying out the scheduled calibration tasks.
3) Deciding calibration periods
Calibrations are usually done:
- Before and after a major critical measuring project
- After the instrument took a hit
- According to the requirement of a particular job
- On a monthly, quarterly, biannual or annual basis
4) Execution
Calibration activities are then executed by the calibration staff who must follow the appropriate instructions, which would include any associated safety procedures.
5) Documentation
The process and the calibrations need to be recorded and documented on a regular basis. This is done to maintain an accurate record on calibration.
6) Analysis
Based on the documented calibration results, equipment managers then have to analyze the data to see if any corrective action needs to be taken.

The need for a calibration management solution
As businesses expand, so do their equipment. This increase in business equipment also increases the amount of manual documentation that needs to be done almost exponentially. In the Power & Energy sector, for example, almost 33% have more than 5,000 instruments that require calibrating. Moreover, around 42% of companies perform more than 2,000 calibrations each year.
According to the same survey, an equipment manager can spend almost half of his or her time on documentation and paperwork. This time can instead be spent on other value-added activities.
A calibration management software (CMS) is a software designed to schedule the calibration of instrumentation and maintenance requirements in all types of industrial settings. It uses a combination of scheduling, history, and communication with field instrumentation to ensure that calibration, adjustments or replacements are performed on a timely basis.
A calibration management solution helps equipment managers to better monitor processing equipment and ensure they are working at their optimal levels. This is done by ensuring that moving parts have lubricants and that consumable products used in a process are replaced in advance. It also provides equipment managers with automated planning options that help reduce administration and management effort.
Core features of a calibration management software
Choosing the appropriate type of software for your organization is a complicated process, especially if you don’t know where to begin. The first factor to consider is the business goals and objectives you want to attain. Next, comes the utilization strategies you would want to adopt in achieving those. Different businesses have different calibration needs.
Listed below are some of the major features you should look for when deciding on a calibration management solution for your organization:
- Identify instruments that need to be calibrated
- Determine calibration requirements
- Establish calibration procedures
- Add, maintain and retrieve master equipment records, and calibration history records
- Automatically schedule future calibration due dates
- Develop corrective action procedures
- Document calibration results and activities
- Compile reports for calibration interval analysis
- Support audit trails for calibration systems to track changes in the database
- Backup and restore data internally
Benefits of a calibration management software
An automated calibration management software offers a variety of benefits to businesses. These range from reduced costs and increased efficiency to greater control over equipment maintenance and management.
Listed below are some of the most highlighted benefits that a calibration management solution has to offer.
1) Automated and streamlined workflows
A CMS tool offers automated planning that serves to reduce the administrative and managerial load. The software helps streamline workflows and assist the calibration managers who are tasked with managing calibration intervals. Their purpose is to make a well-researched and qualified recommendation. Equipment engineers are also given the ability to optimize calibration intervals using the software’s ‘History Trend’ function.
In addition to this, manual procedures are replaced with automated and validated processes. Equipment managers no longer require pens and paper. Calibration instructions are created using the software to guide engineers through the calibration process. These instructions can also be downloaded to a technician’s handheld documenting calibrator while he is on the field.
2) Improved efficiency
As the entire calibration process becomes more streamlined and automated, plant efficiencies also improve. As the manual procedures are replaced with automated ones, businesses can save time in a lot of labor-intensive calibration activities. Engineers are freed up to perform more strategic analysis or other important value-added activities.
3) Cost reduction
Implementing a software-based calibration management helps businesses reduce the overall costs. These savings come from the now paperless calibration process, with no manual documentation procedures. Moreover, a CMS solution enables faster, easier and more accurate analysis of calibration records and identifying historical trends. Plants can, therefore, reduce costs and optimize calibration intervals.
4) Performance management
A calibration management program can help equipment managers keep track of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in real-time, while also giving them a detailed view of operations. Performance of the installed equipment and resources can be analyzed across the entire organization.
5) Compliance with regulations and standards
Regulatory organizations and standards such as FDA and ISO place demanding requirements on calibration data records. A calibration management software has many functions that help in meeting these requirements. A CMS solution helps track compliance with calibration timeliness, according to FDA and ISO. It makes sure that the guidelines and standards are met accordingly.
6) Maintain records and history of use and calibration
Procedures and calibration strategies are planned. All calibration assets are managed automatically by the calibration management software. The program also maintains a device’s position and calibrator databases while also setting up automatic alerts for scheduled calibrations. The software also automates report generation and centralizes calibration data storage.
7) Equipment longevity
Planning and keeping track of equipment maintenance can be a really tiring task. A lot of resources, both time and money, are invested in ensuring equipment longevity. A CMS solution can automatically calculate an item’s due date for calibration and maintenance according to the user-defined intervals.
A calibration management software gives equipment managers the ability to define how they want the due date calculated and set the calibration frequency to any number days, months or years. In addition to this, downtime will be greatly reduced as your equipment is calibrated and maintained on schedule, saving your business both time and money.
Implementation of a calibration management software
Now that we’ve discussed the benefits of a calibration management software, it is important to know how to successfully incorporate a CMS app into your business. A successful implementation requires an understanding of how your current workflows are going to fit in the software. Below we have listed some tips that will help you implement a calibration management solution, effectively.
1) Highlight your goals
Before adopting a CMS solution, it is important for businesses to define their goals and highlight their calibration needs. Whatever your objectives are, it is important to define them. Once done, then adopt a calibration management solution accordingly. Without clear goals, you cannot hope to achieve any clear success with your software implementation.
2) Self-analysis
Self-assessment is used by businesses to both assess an organization’s current situation and to create strategies for improving that situation. A self-evaluation can also provide businesses with information on the value, kind and quantity of equipment that it owns and of its current status. A self-assessment by analyzing the current situation of the company will also help set the baseline to judge future performance after the software is implemented.
3) Define your calibration needs
Before a calibration management software can be deployed, it is important to define your calibration needs. Knowing the type of equipment you own and your calibration needs are extremely important when choosing a CMS solution for your organization.
4) Choosing a software
Once your goals and calibration needs are defined, you can then look for a software with relevant features that can help you fulfill these needs and achieve your organizational goals.
5) Monitor, review, and update
Once a calibration management software is deployed, you need to monitor some key performance indicators in order to judge whether the deployed solution has brought about expected levels of success.
To determine whether the system is performing as projected, data on the condition and performance of assets need to be captured and analyzed on a regular basis. For example, you can generate reports to identify the maintenance schedules and life cycles of your equipment and use it to reduce downtime. In addition to this, you can take regular feedbacks from crew members and generate performance reports. With this data, you can update the calibration management program accordingly to ensure maximum efficiency.
Conclusion
Every type of process plant, regardless of size and industry sector, can benefit from implementing an automated calibration management software. Compared to traditional, paper-based systems, using a dedicated CMS solution results in improved quality, increased productivity and reduced costs of the entire calibration process. This in return saves businesses both time and money and complements its growth.



